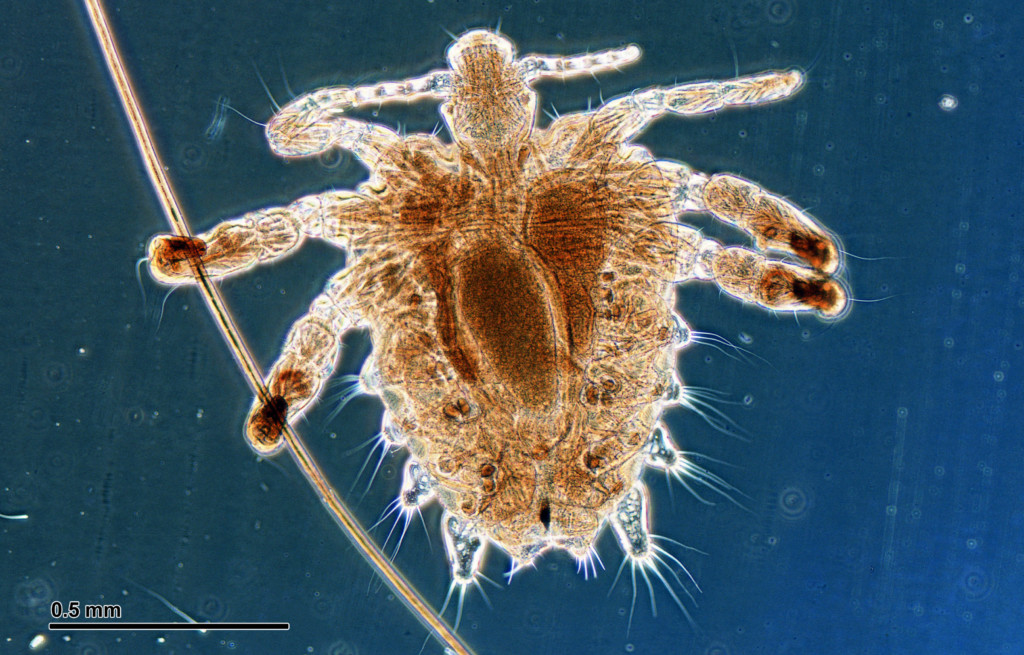
Pubic lice are a taboo topic but they affect millions of people worldwide. These parasitic insects are embarrassing and uncomfortable but understanding them can lead to better health. Let’s shed light on the causes, symptoms, and treatment options so you can tackle this common problem.
Pubic lice or the std slang term “crabs” are small insects that live in coarse body hair, especially in the genital area. They spread pubic lice primarily through intimate, person-to-person contact, notably during sexual interactions, and can also be transmitted through contact with infested items like clothing and bedding. Despite the social stigma, they are not exclusive to any particular group so awareness and education are key to prevention.
This article will cover everything you need to know about pubic lice from their characteristics and how they are transmitted to diagnosis and treatment options. By reading this you can take steps to prevent and manage and be healthier and more informed about sexual health.
What is Pubic Lice?
Pubic lice, commonly known as crabs, are tiny insects that infest the pubic or genital area of humans. These parasites are one of the three types of lice that live on humans, the other two being head lice and body lice. Unlike head lice, which are found on the scalp, and body lice, which live in clothing and bedding, pubic lice prefer coarse body hair in infested areas. Primarily found in pubic areas, it also includes hair on the legs, armpits, mustache, beard, eyebrows, and even eyelashes.
Adult pubic lice are small, grey-colored, and crab-shaped, which is why they are often referred to as crabs. These tiny insects feed on human blood to survive, causing itching and discomfort in the affected areas. Despite their small size, they can cause significant irritation and require prompt treatment to eliminate.
Pubic Lice Characteristics in Pubic Hair
Pubic lice, or pubic louse, are a type of lice that infest coarse hair. Unlike head and body lice, pubic lice are small parasites that feed on human blood.
- Size and Appearance: Adult pubic lice are small, 1.1–1.8 mm. They are crab-shaped that’s why they are sometimes called “crabs.”
- Habitat: They live in pubic hair but can also live in armpits, chest hair, or beards.
Causes and Risk Factors
The following are causes and risk factors to catching pubic lice:
- Sex with multiple partners
Having sex with multiple partners increases your chances of running into someone with pubic lice since sex is the main way they are transmitted. - Close Contact
Non-sexual close contact, such as hugging or cuddling, with an infested person can also spread lice. - Sharing Personal Items
Sharing clothes, towels or bedding with someone who has pubic lice can spread the infestation, but this is less common than direct contact. - Living in Close Quarters
Places where people live in close quarters and share personal items, such as dorms or shelters, can spread pubic lice. - Lack of Awareness
People who are not aware of pubic lice symptoms or prevention methods can spread them to others through contact or shared items. - Age Group
Adults, especially the sexually active, are the most affected age group. Infestation in children may mean close non-sexual contact or shared items like bedding. - Travel and Shared Accommodations
Traveling and staying in accommodations where bedding and towels are shared or not properly cleaned can increase your chances of getting lice. - Limited Access to Treatment
Individuals with limited access to healthcare or proper lice treatments are at a higher risk of prolonged infestations, increasing the likelihood of transmission.
How does Pubic Lice Spread?
Pubic lice or crab lice spread in many ways. Understanding these ways can help you prevent infestation. This guide will cover how pubic lice spread through sex, personal contact, and infested clothing.
Through sexual contact
Pubic lice are more often transmitted through sex. Physical contact increases the chances of lice moving from one person’s coarse hair to another’s. Whether it’s hair in the groin area or other body hair, close contact during sex makes it easy for lice to spread.
Through personal contact
Beyond sex, pubic lice can spread through body contact with an infected person. Hugging or close cuddling is casual contact that can transfer lice to a new host. Be aware of itching and other symptoms of pubic lice in yourself and your partner.
Through shared items
While rare, pubic lice can spread through shared items like clothing, bedding, or towels. If shared with an infected person these items may have lice or lice eggs. Washing shared items in hot water can help prevent the spread of lice. Be mindful of sharing personal items to avoid pubic lice infestation.
Symptoms of Pubic Lice Infestation
It’s important to recognize the symptoms early to treat. Here are the signs:
Intense Itching
One of the most obvious symptoms of pubic lice is severe itching. This itching is caused by lice bites as adult pubic lice feed on human blood. This itching is usually worse at night and can disrupt sleep. If you have unusual itching in your pubic area, check for other symptoms too.
Irritation and Inflammation
Irritation and inflammation are common reactions to pubic lice. Scratching due to itching can cause red inflamed skin. This can also result in blue spots where the lice have bitten. Irritation can extend to any coarse hair including the areas around the thighs and abdomen.
Visible lice and eggs
Another obvious symptom is seeing visible lice or their eggs, also known as nits, in the grown region. Adult pubic lice are tiny but visible, often looking like small crab-like creatures. Lice eggs look like small white or yellow dots attached to hair shafts.
How to Diagnose Pubic Lice
Diagnosing pubic lice through visual inspection is important to treat and prevent the spread. Let’s see how you can identify these annoying creatures.
Visual Inspection Methods
Visual inspection is the first step in diagnosing pubic lice. Here’s how:
- Look for Lice: Adult pubic lice are tan or grayish-white and about the size of a pinhead. You might see them moving in the pubic hairs.
- Check for Lice Eggs: Lice eggs or nits are tiny yellow, tan, or brown dots attached to the base of the hair shafts. They are easier to see than adult lice.
- Identify Lice Bites: Look for blue spots on the skin. These are often bites or rashes caused by allergic reactions to lice saliva.
- Use a Fine-Toothed Comb: Run a comb through pubic hair to catch any visible lice.
See a Doctor
If you’re not sure if you have pubic lice, it’s best to see a doctor. Here’s why:
- Proper Diagnosis: Professionals use special tools and methods to confirm the infestation.
- Treatment: They can prescribe lice-killing lotions or shampoos, often containing piperonyl butoxide.
- Prevention: You will learn how to prevent lice from spreading to partners through sex or through body contact.
- Further Testing: If needed, a sexual health clinic or primary care doctor can test for other STIs.
Treatments for Pubic Lice
Over-the-counter treatments, prescription meds, and home remedies for pubic lice are all options. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider before starting any pubic lice treatment to ensure safety and effectiveness.
OTC treatments
For many, OTC pubic lice treatments are the first step in managing pubic lice. These can be found at most drugstores:
- Lice-killing lotion: Look for lotions with pyrethrin and piperonyl butoxide. Apply to the affected area and leave for the recommended time to kill adult pubic lice and lice eggs.
- Permethrin cream: 1% lotion is effective for pubic lice. Follow the instructions carefully.
Prescription meds
If OTC treatments don’t work, a doctor may prescribe stronger meds. Some are:
- Malathion lotion: Known as Ovide, this is applied to hair for lice and left for a period before washing off. It’s effective but use as directed.
- Ivermectin: Taken as a pill, this is an option if topical treatments don’t work.
Home remedies and their success rate
While OTC and prescription meds are recommended, some try home remedies. But these remedies have no proof of success:
- Vinegar: Some say vinegar can remove lice eggs but not adult lice.
- Olive oil: Claimed to smother lice but no proof.
- Tea tree oil: Praise for its natural lice-killing properties but results are hit and miss.
For best results stick to proven treatments and see your healthcare provider. Don’t forget to wash everything in hot water and clean your personal items to prevent re-infestation.
Complications and Considerations
While pubic lice primarily cause severe itching, redness, and irritation in the affected area, there can be additional complications if left untreated. Persistent scratching due to bites can lead to secondary skin infections, which may require further medical treatment. Therefore, it is crucial to treat pubic lice infestations promptly to avoid these complications.
Although pubic lice do not transmit diseases, their presence can be an indicator of other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). If you are diagnosed with pubic lice, it is advisable to get tested for other STIs as a precaution. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their healthcare provider before using any lice treatment to ensure it is safe for them and their babies.
Sex Partners and Pubic Lice
If you have pubic lice, it’s essential to inform your partners about the infestation. Pubic lice are usually spread through sexual contact, and your partners may also have contracted the infection. It’s crucial to treat all sexual partners from the previous two months to prevent the spread of pubic lice. This includes both current and past partners, as pubic lice can survive for up to 24 hours off a human host.
When informing your sexual partners, be honest and open about the infestation. It’s essential to use “I” statements to avoid blame or shame. For example, you can say, “I’ve recently been diagnosed with pubic lice, and I want to inform you so we can take steps to prevent the spread.” Encourage your partners to seek medical attention and get treated for pubic lice.
Remember, pubic lice are a common problem, and it’s not a reflection of your personal hygiene or sexual behavior. By being open and honest with your sexual partners, you can help prevent the spread of pubic lice and protect your sexual health.
Pubic Lice and Pregnancy
If you’re pregnant and have pubic lice, it’s essential to seek medical attention immediately. Pubic lice can cause discomfort and itching, which can be challenging to manage during pregnancy. However, the good news is that pubic lice do not pose a significant risk to the unborn baby.
When treating pubic lice during pregnancy, it’s crucial to use medications that are safe for both the mother and the baby. Your healthcare provider may recommend a permethrin-based cream or lotion, which is commonly used to treat pubic lice. However, it’s essential to follow the instructions carefully and avoid using any medications without consulting your healthcare provider.
In addition to treating pubic lice, it’s essential to practice good hygiene during pregnancy. This includes washing your clothes, bedding, and towels in hot water and drying them on high heat. You should also avoid sharing personal items, such as towels or clothing, with others.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively manage and treat pubic lice during pregnancy, ensuring both your comfort and the health of your baby.
Prevention
Preventing pubic lice involves several steps. These steps reduce your risk of infestation and promote personal hygiene. Below are the tips to remember:
Good hygiene
Good hygiene is key to preventing pubic lice. Regular showers and washing clothes can remove lice and lice eggs. Use hot water when washing clothes, lice can’t survive high temperatures.
- Shower regularly.
- Wash clothes in hot water.
- Practice personal hygiene.
Avoid infested individuals
Direct body contact with an infected person is the main way pubic lice spread. Avoid sexual contact with infested individuals to reduce your risk. If someone you know has symptoms of pubic lice such as intense itching or blue spots, keep distance.
- Don’t have intimate contact with infected individuals.
- Don’t share towels or clothes.
- Be careful in intimate settings.
Laundry instructions for clothing and bedding
If you suspect a lice infestation, clean your clothes and bedding properly. Wash infected items in hot water and dry on the highest heat. This will kill lice-killing lotion, lice eggs, and adult pubic lice.
- Hot water for washing.
- High heat for drying.
- Clean all personal items used recently.
By following these tips you can reduce your risk of pubic lice and maintain your sexual health. Cleaning and avoiding infested individuals are the key to prevention.
In summary, pubic lice may seem like a taboo subject but understanding them is key to good sexual health and hygiene. Knowing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options means you can deal with infestations quickly and effectively and reduce discomfort and complications. Remember pubic lice are common and not a reflection of your personal hygiene or lifestyle. Taking precautions, seeking treatment in time, and talking to your sexual partners are the key to managing this condition. With the right approach, you can protect yourself and others and raise awareness and understanding of this often overlooked health issue.
FAQs
Can you get pubic lice without being sexually active?
Yes, it is possible to get pubic lice without being sexually active. While sexual contact is the most common way pubic lice spread, they can also be transmitted through non-sexual means. This includes sharing infested clothing, bedding, or towels. If you come into contact with items that an infected person has used, you may catch pubic lice.
Are body lice and crabs the same thing?
Pubic lice, primarily known as crabs, reside within the genitals. They are a different type of lice compared to head lice. The pubic lice were nicknamed because the bodies looked like small crabs.
Do the STD crabs still exist?
Yes, STD crabs, or pubic lice, still exist and continue to affect millions of people worldwide each year. Despite being part of the same parasitic family as head lice and body lice, pubic lice are distinct in their habitat and characteristics. They are primarily found in the pubic or genital area, and are commonly spread through sexual contact.
What do sex crabs look like?
Sex crabs, or pubic lice, are tiny insects that are crab-shaped, which is why they are often referred to as crabs. Adult pubic lice are small, about 1.1–1.8 mm in size, and have a tan or grayish-white color. They have six legs, with the front two legs being larger and resembling crab claws, which help them cling to coarse body hair.
What happens if crabs are left untreated?
If pubic lice, commonly known as crabs, are left untreated, they can lead to several complications. The most immediate consequence is persistent intense itching and irritation caused by lice bites as they feed on human blood in the pubic region. This itching can result in constant scratching, which may lead to skin damage and secondary bacterial infections.
Moreover, untreated pubic lice can continue to spread to other coarse body hair, such as armpits and chest hair, increasing the discomfort and area of infestation. Continuous infestation can also lead to emotional distress and embarrassment due to the stigma associated with pubic lice.
What kills pubic lice naturally?
While there are no scientifically proven natural remedies to completely eliminate pubic lice, some people use natural methods alongside conventional treatments to help manage infestations. These methods may include:
- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its natural insecticidal properties, tea tree oil is sometimes used to help reduce lice. Dilute a few drops in a carrier oil and apply to the affected area, but be cautious of skin sensitivity.
- Vinegar: Some suggest using vinegar to loosen lice eggs (nits) from hair shafts. Apply vinegar to the pubic hair and leave it for a short period before combing out the nits.
- Salt and Vinegar: Taking a warm bath with salt and vinegar might help soothe the skin and reduce irritation, although it won’t kill lice.
Sources:
National Library of Medicine: Pubic lice: an endangered species?