Male yeast infection occurs when the Candida fungus overgrows, causing symptoms like itching, redness, and discomfort. In this article, we’ll cover the symptoms, causes, and treatments to help you manage this common condition effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Male yeast infections often present with symptoms such as inflammation, a burning sensation, itchiness, redness, and a thick, white discharge; recognizing these symptoms may aid in early detection and treatment.
- The primary cause of male yeast infections is an overgrowth of Candida albicans, often linked to poor hygiene, weakened immune systems, and disruption of microbial balance due to factors like antibiotics.
- Effective treatment involves antifungal medications and good hygiene practices, with prompt medical attention necessary to prevent complications from untreated infections.
Recognizing Male Yeast Infection Symptoms
Diagnosing male yeast infections can be difficult because they may present with symptoms similar to those of other medical issues. There are distinct indicators frequently linked with penile yeast infections. These signs include swelling and a burning sensation on the penis, as well as itching, tenderness, and redness. A hallmark symptom is the presence of a thick white discharge that often collects in the folds of the penile skin.
When experiencing such indications:
- Inflammation
- A burning feeling on the penis
- Itching
- Tenderness
- Redness
- A dense white discharge in the penile skin creases
It’s important to note that these symptoms usually accompany an unpleasant itchiness alongside a characteristic white discharge—a clear signpost pointing towards a yeast infection. Early identification of these warning signals is essential for effective management and circumventing complications arising from untreated infections.
Swift recognition plays an indispensable role when dealing with male yeast issues—being vigilant about prevalent symptoms empowers men to seek timely intervention while avoiding needless discomfort. Bear in mind that these manifestations might occasionally mimic those associated with different health afflictions.
Differentiating from Other Conditions
Symptoms indicative of a male yeast infection might be confused with those of other health conditions, such as jock itch or sexually transmitted infections.
The symptoms that could appear similar include:
- Reddish skin
- Discomfort
- Inflammation
- Irritation
Such commonalities can make it difficult to pinpoint the exact illness without seeking medical advice.
One characteristic is offensive-smelling discharge and discomforting swelling at the head of the penis, which tend to be more characteristic signs associated with male yeast infections. A visit to a healthcare provider is crucial for making an accurate diagnosis. During your consultation, your reported symptoms will typically be evaluated. They may collect a sample from either the discharge or the affected area on your skin for laboratory analysis to confirm their findings.
A misdiagnosis can lead to unsuitable treatment options that might not only fail in addressing your issue but also potentially worsen it. Thus, scheduling time with either a urologist or a primary care physician is vital in securing an accurate diagnosis and an effective course of treatment.
Let’s now explore the causes and risk factors that increase the likelihood of male yeast infections.
Causes and Risk Factors for Male Yeast Infections
Understanding the origins and risks of male yeast infections is crucial for their prevention and management. Poor hygiene, especially inadequate cleansing of the genital area, is a significant cause. Men with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to these infections, and chronic illnesses like diabetes and obesity increase this vulnerability.
In women, an imbalance of fungi and bacteria can lead to vaginal yeast infections. The overuse of antibiotics may disrupt the balance of microorganisms. Sexual activity with someone infected can transmit Candida to males.
Recognizing these risk factors and using preventive strategies can reduce the chances of yeast infection. Next, we focus on Candida albicans, the main pathogen causing most candidal infections.
Candida Albicans: The Culprit Fungus
Most yeast infections, affecting women and men, are caused by the fungus Candida albicans. The genital area is particularly susceptible to infection due to its warm, damp conditions. Understanding this fungus helps manage and prevent future infections.
Within certain regions of our bodies, like the digestive tract and skin, it’s common to find Candida albicans coexisting harmlessly. Nevertheless, when there’s an imbalance in our body’s natural microbial population, this can prompt an overgrowth of Candida, leading to symptoms such as an itching sensation, redness around the affected area, and discomfort that characterizes an active yeast infection.
By acknowledging what can cause increased fungal growth, such as environments with excessive moisture or a disrupted bacterial balance, proactive measures can be taken to prevent and manage these types of infections. Subsequently, we will explore how men might acquire these infections, as well as the factors that contribute to their increased risk.
How Men Get Yeast Infections
Men can contract yeast infections in various ways, making understanding them crucial for prevention. Sexual intercourse with a partner who has a vaginal yeast infection is a common method that can transmit Candida and cause a penile yeast infection.
Candida balanitis is more commonly seen in uncircumcised men. Utilizing strong soaps or not properly drying off after washing may foster an environment conducive to male yeast infections.
Yeast-induced balanitis is prevalent among men and poses potential complications if not addressed promptly. Awareness of associated risk factors, coupled with maintaining excellent genital hygiene practices, plays a significant role in diminishing the likelihood of contracting a male yeast infection.
With this understanding, let us explore available treatment options for combating male yeast infections effectively.
Effective Treatments for Male Yeast Infections
To effectively manage male yeast infections, employing antifungal treatments in conjunction with good hygiene practices is essential. Typical treatment includes the application of topical antifungal creams such as miconazole, clotrimazole, or nystatin and may involve oral antifungals like Diflucan if necessary. It’s advised that these medications be used twice a day for a period ranging from 10 to 14 days to achieve optimal results.
At times when symptoms persist despite using topical agents, physicians might prescribe oral antifungals such as Diflucan. While undergoing treatment, one should abstain from sexual intercourse and opt for mild hygiene products to avoid Irritation. It’s crucial to adhere strictly to the prescribed regimen of antifungal medication even when there appears to be an early improvement in symptoms.
It is essential not only to know when, but also how, to seek professional medical advice. This is especially true for untreated yeast infections, which can escalate into more serious issues if neglected. Engaging your healthcare provider promptly ensures proper management of the condition.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
If symptoms of a male yeast infection, such as discomfort, swelling, and abnormal discharge, worsen or do not improve after initial treatment, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider. Untreated yeast infections can lead to serious complications like invasive candidiasis and systemic issues, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems.
In cases where your symptoms persist or worsen despite initial treatments, seeking immediate medical attention is advisable, as this may indicate the presence of a more persistent and potentially resistant infection. Repeated instances of male yeast infections necessitate consultation with a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies.
Recognizing when to seek medical help can mitigate the effects of unresolved yeast infections. Now, let’s focus on preventive measures against future male yeast infections.
Preventing Male Yeast Infections
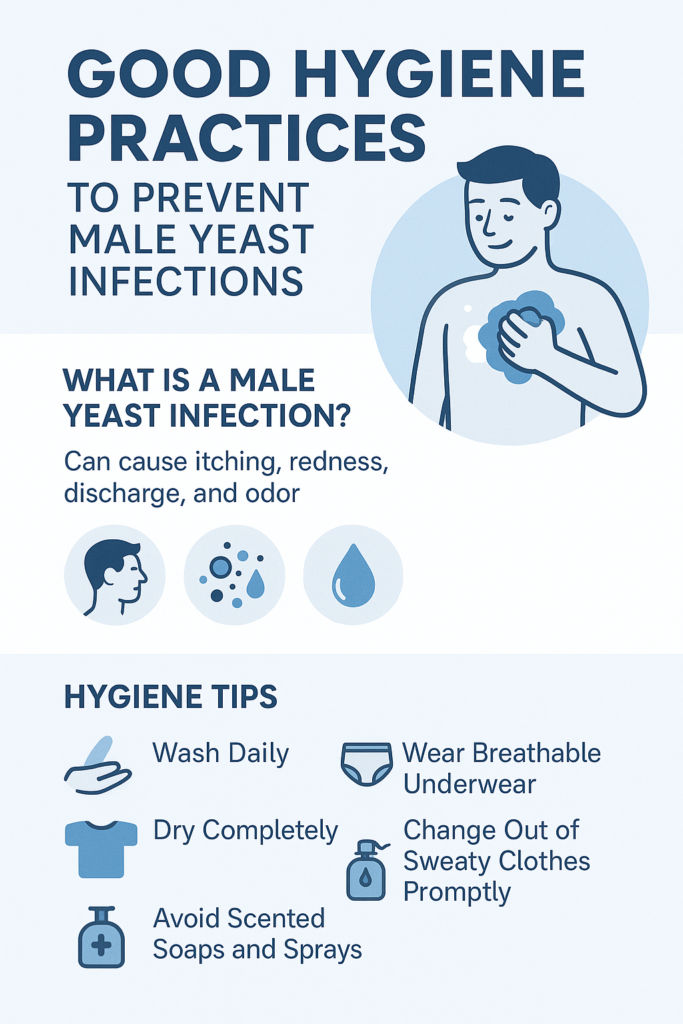
To prevent male yeast infections, maintain good hygiene and make lifestyle changes. Daily showers, breathable clothing, and ensuring the groin area is dry after washing can help prevent infection.
Clean and sanitize garments or towels used during infection to prevent recurrence. Regularly wash personal items like underwear separately to maintain good hygiene.
By integrating these preventative steps into your everyday habits, you stand a much better chance of avoiding the development of a yeast infection. It’s also crucial to promptly treat any onset of infection to avoid further complications.
Complications of Untreated Yeast Infections
Untreated male yeast infections can lead to complications, including serious health conditions and painful symptoms. One such complication is invasive candidiasis, a severe yeast infection that may enter the bloodstream and affect vital organs such as the heart, lungs, brain, and esophagus.
While some untreated yeast infections may resolve on their own, they can still lead to significant complications, including symptoms like weakness, fatigue, and a weakened immune system. If serious complications arise from a yeast infection, aggressive treatment with intravenous antifungals may be required.
Understanding the potential complications of untreated yeast infections highlights the importance of seeking timely treatment. Now, let’s explore how to manage recurring yeast infections effectively.
Managing Recurring Yeast Infections
To manage yeast infections, employ a holistic strategy that treats both partners and emphasizes hygiene. If one partner has an infection, the other should also receive treatment to reduce the risk of recurrence. Unprotected intercourse and poor hygiene can result in repeated male yeast infections.
Nearly half (48%) of those with Candidal balanoposthitis may experience recurring episodes. If yeast infections persist after treatment, a prolonged regimen of daily treatments for weeks and weekly treatments for several months may be necessary.
These methods help control and prevent yeast infections, promoting better health and comfort. Key elements include:
Summary
Male yeast infections are common but often overlooked. Identifying early signs—irritation, inflammation, and white discharge—is essential for timely treatment. Understanding causes like poor hygiene and weakened immune systems can help prevent these infections.
Effective remedies exist for male yeast infections, such as antifungal creams and pills. It’s essential to complete the prescribed treatment. If symptoms persist or recur, consult a healthcare provider. Preventative measures include maintaining good personal hygiene and keeping the genital area dry after washing; these steps greatly reduce infection risk. Men who manage recurring yeast infections enhance their well-being by avoiding discomfort associated with this condition.
FAQs
What are the common symptoms of a male yeast infection?
Common symptoms of a male yeast infection include itchiness, soreness, redness, and a thick, white discharge that may accumulate in skin folds.
How can I prevent male yeast infections?
To effectively prevent male yeast infections, maintain good hygiene by taking daily showers, wearing breathable fabrics, and ensuring the groin area is thoroughly dried after bathing.
When should I see a healthcare provider for a yeast infection?
You should see a healthcare provider for a yeast infection if your symptoms worsen, do not improve with initial treatments, or if you experience recurrent infections.
What causes male yeast infections?
Male yeast infections can be caused by poor hygiene, a weakened immune system, chronic conditions such as diabetes and obesity, an imbalance of fungi and bacteria, the overuse of antibiotics, and sexual contact with an infected partner.
Are there complications associated with untreated yeast infections?
If yeast infections are not promptly addressed, they can escalate into severe issues such as invasive candidiasis, endangering essential organs and requiring aggressive therapy.
Sources
Mayo Clinic – Can Men Get Yeast Infections? https://www.webmd.com/men/can-men-get-yeast-infections
Healthgrades – Male Yeast Infection: How to Treat Jock Itch and More https://resources.healthgrades.com/right-care/mens-health/male-yeast-infection
Mayo Clinic – Yeast infection in men: How can I tell if I have one? https://www.mayoclinic.org/male-yeast-infection/expert-answers/faq-20058464
